When building or upgrading a PC, performance is key—especially for gamers, creators, and professionals who rely on speed and graphics power. One term you might encounter during research or troubleshooting is “GPU bottleneck.” But what does it really mean? Is it bad? Can it be fixed?
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about GPU bottlenecks, including:
- What a GPU bottleneck is
- How to detect it
- Why it happens
- Tips to fix and prevent it
- The difference between GPU and CPU bottlenecks
- Tools to test for GPU bottlenecks
- Best practices for balancing your system
Let’s dive into the world of graphics performance optimization.
What is a GPU Bottleneck?
A GPU bottleneck occurs when your graphics processing unit (GPU) is unable to keep up with the demands of your CPU or the application being run—especially in high-performance scenarios like gaming or 3D rendering. It becomes the limiting factor, preventing your system from achieving its full potential.
Real-Life Analogy:
Imagine your PC as a factory assembly line. If the GPU is slower than the rest of the components (like the CPU or RAM), it causes a traffic jam in the workflow. This delay means your system isn’t performing as efficiently as it should.
Why Do GPU Bottlenecks Happen?
Several factors can lead to a GPU bottleneck. Understanding these helps prevent issues during system building or troubleshooting.
1. Unbalanced Hardware Pairing
If you pair a powerful CPU (like the Intel i9 or Ryzen 9) with an entry-level or outdated GPU (e.g., GTX 1050), the GPU becomes the weak link. Your CPU may process game logic, AI, and background tasks quickly, but the GPU can’t render frames at the same speed.
2. Running at High Resolutions or Settings
Games rendered at 1440p or 4K with ultra settings demand a lot from the GPU. Even high-end cards like the RTX 3070/3080/4090 can struggle in some modern AAA titles if pushed beyond their limits.
3. Outdated GPU Drivers or Firmware
Driver incompatibilities, outdated software, or BIOS issues can cause the GPU to underperform—even if it’s relatively modern.
4. Thermal Throttling
Overheating can cause the GPU to slow down its clock speed to prevent damage, leading to a bottleneck. Dust buildup, poor airflow, and aging thermal paste are common culprits.
5. Software Optimization
Some games or programs are not optimized for specific GPUs or drivers. Poor optimization can force the GPU to work harder than it should.
How to Detect a GPU Bottleneck
Here are some signs that your GPU may be bottlenecking:
✅ Common Symptoms:
- High GPU usage (95–100%) while CPU usage remains low
- Low or inconsistent frames per second (FPS)
- Game stuttering or screen tearing
- Long rendering times in creative applications
- System temperature spikes when launching GPU-intensive software
🔧 Tools to Use:
You can use software tools to monitor system performance in real-time:
- MSI Afterburner (GPU usage, temperature, clock speed, FPS overlay)
- GPU-Z (GPU health and specs monitoring)
- HWMonitor (Tracks CPU/GPU temperatures and loads)
- Task Manager (Quick look at resource usage)
- UserBenchmark or Bottleneck Calculator (Estimates component pairing efficiency)
GPU Bottleneck vs. CPU Bottleneck
While a GPU bottleneck happens when the GPU slows down your system, a CPU bottleneck is the opposite—the processor becomes the limiting factor.
🧠 CPU Bottleneck:
- High CPU usage (90–100%)
- Low GPU usage
- Usually occurs in strategy games, simulations, or open-world titles with many NPCs or complex calculations.
🎮 GPU Bottleneck:
- High GPU usage
- Lower CPU usage
- Happens in graphically intensive games and applications, especially at high resolutions or settings.
Tip: Bottlenecks are normal to an extent. No system is perfectly balanced at all times across all tasks. The goal is to minimize bottlenecks, not eliminate them entirely.
How to Fix or Reduce a GPU Bottleneck

Let’s explore ways to resolve a GPU bottleneck without breaking the bank:
1. Lower In-Game Graphics Settings
Reduce or disable settings such as:
- Shadow Quality
- Anti-Aliasing
- Ambient Occlusion
- Ray Tracing
- Texture Resolution This directly reduces the load on your GPU.
2. Lower the Game Resolution
If you’re gaming at 4K or 1440p, try stepping down to 1080p. This dramatically lowers the number of pixels your GPU has to render.
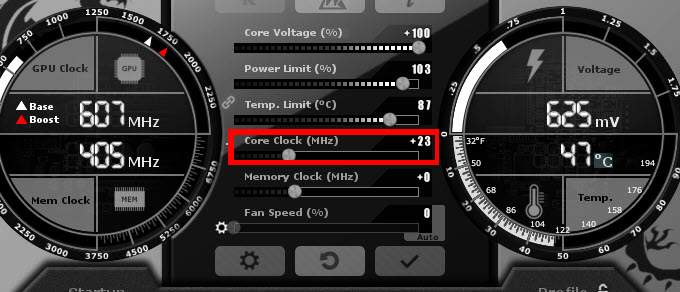
3. Overclock Your GPU (With Caution)
Tools like MSI Afterburner allow mild overclocking to boost performance. However, ensure proper cooling and stability to avoid crashes.
4. Update GPU Drivers
NVIDIA and AMD regularly release driver updates that include performance improvements and bug fixes. Always keep your drivers up to date.
5. Improve Cooling and Airflow
Ensure your PC has good ventilation, clean fans, and fresh thermal paste if the GPU is older. Lower temperatures mean more consistent performance.
6. Close Background Applications
Apps like Chrome, Discord, or recording software can eat up GPU memory. Free up resources before launching heavy games or software.
7. Upgrade Your GPU
If all else fails and your card can’t meet modern requirements, it may be time to upgrade. Match your new GPU with your CPU to ensure balanced performance.
How to Prevent GPU Bottlenecks When Building a PC
When designing a new rig, take these steps to avoid future GPU bottlenecks:
🔍 Research Before Buying
- Look at benchmarks for the games or apps you’ll be using.
- Use PCPartPicker or bottleneck calculators to test component compatibility.
🎯 Match Components Based on Performance Tiers
- Pair mid-tier GPUs (like RTX 3060/4060) with Ryzen 5 or Intel i5 CPUs.
- High-end GPUs (like RTX 4090) should go with Ryzen 9 or Intel i9 to avoid CPU bottlenecks.
🧠 Consider Your Use Case
- Gamers: Focus on GPU strength for high-res or high-refresh-rate gaming.
- Creators: Ensure the GPU supports CUDA/OpenCL or whatever your software requires.
- Streamers: Consider both CPU and GPU load if doing real-time encoding.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What does a GPU bottleneck mean in a computer system?
A GPU bottleneck occurs when your graphics card is working at full capacity while other components, like the CPU, are underutilized. This means the GPU is slowing down the system’s overall performance, especially in graphics-heavy tasks like gaming or video rendering.
2. Is it bad if my GPU is constantly at 95% usage?
Not necessarily. A 95% GPU usage means your graphics card is being fully utilized, which is normal during demanding tasks. However, if your frame rates are still low or stuttering occurs, it could indicate a bottleneck, especially if your CPU and RAM aren’t being pushed as hard.
3. How can I tell if my GPU is being bottlenecked?
To check for a GPU bottleneck, monitor your system using tools like MSI Afterburner or Task Manager. If your GPU is at 99–100% usage consistently while your CPU remains under 60–70%, it suggests your GPU is the limiting factor. Also, look for signs like low FPS and lag during gameplay.
4. What does it mean when GPU usage is at 99%?
99% GPU usage indicates your graphics card is working at near full capacity. This is typical in many games, especially at high settings. However, if performance is still lacking or the CPU is barely used, it could be a sign of a GPU bottleneck.
5. Can a GPU bottleneck affect gaming performance?
Yes, a GPU bottleneck can reduce your gaming performance by limiting frame rates, causing lag, or creating stutter in gameplay. It happens when the graphics card can’t process frames fast enough to match what the CPU is delivering, especially at high resolutions or in poorly optimized games.
Conclusion
A GPU bottleneck can affect performance, user experience, and your enjoyment of games or creative work. But with the right knowledge, you can easily detect, reduce, or prevent bottlenecks by adjusting settings, upgrading hardware, or optimizing your software. By ensuring your system is well-balanced and properly maintained, you’ll enjoy smoother performance, better visuals, and a more efficient workflow.